Dengsheng Chen (陈登盛)
About Me
I am a Generative AI Researcher at ByteDance~(TikTok), focusing on video generation and unified multimodal modeling. My recent work explores a unified autoregressive (AR) generative framework built upon continuous token representations, aimed at establishing a scalable foundation for multimodal generation. This framework has yielded notable improvements in high-fidelity image synthesis, and my ongoing efforts extend these advances to audio and video generation, with an emphasis on temporal consistency, cross-modal alignment, and controllability.
Last updated: Nov. 16, 2025 · Feel free to reach out via email
Educations
Master's degree in computer science, 2019.9-2021.12
College of Computer Science and Technology, National University of Defence Technology (国防科技大学 计算机学院)
Bachelor's degree in computer science, 2015.9-2019.6
College of Mathematics and Computer Science, Fuzhou University (福州大学 数学与计算机科学学院)
Experiences
ByteDance, 2025.2-now
- Video Diffusion Model: (a) Do post-training and DPO/ReFL optimization for a high-resolution image-to-video diffusion model. The model has achieved state-of-the-art performance in commercial applications and is now widely deployed across non-China regions for large-scale video generation.
- Unified Multimodal Model: (a) Developed a unified understanding-and-generation framework based on continuous tokens, introducing a new self-token-prediction generative paradigm. (b) Attained strong performance in image synthesis, with ongoing efforts to enhance audio and video generation quality.
- Infrastructure: (a) Built a multimodal data processing framework supporting distributed data processing and visualization, along with various flexible data-loading modes (e.g., dynamic duration, dynamic resolution, multi-task, multimodal mixed loading, batch-grouped or sequence-grouped training). (b) Designed and implemented a new training framework for scaling Unified Multimodal Model training, enabling efficient resource utilization and multi-task training for models with tens of billions of parameters.
Meituan, 2022.6-2024.11
AIGC & Multimodal: (a) Led the initial training of foundational text-to-image and text-to-video models, contributing to the development of state-of-the-art generative models. (b) Advanced the creation of a unified multimodal model architecture that integrates autoregressive models for both generative and understanding tasks, enhancing performance across multiple modalities. Data Curation: (a) Spearheaded the design and development of an innovative DataCuration framework, enabling seamless handling of image and video data. (b) Engineered a unified data packaging format and user-friendly front-end visualization interface to streamline data management processes. (c) Enhanced the framework with capabilities for automatic data captioning and filtering, thereby supporting sophisticated text-to-image and text-to-video generation workflows. Applications: (a) Explored and applied stable diffusion and stable video diffusion technologies to develop novel solutions for the creative industry. (b) Developed dynamic product imagery and content generation systems with distinctive identifiers, driving intelligent and creative business applications.
ByteDance, 2021.1-2021.12 (Intern)
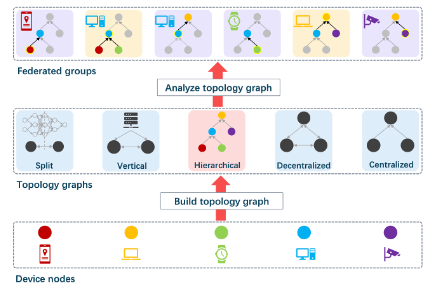
Federated Learning: (a) Contributed to algorithm optimization and the development of federated learning systems, enhancing privacy-preserving machine learning techniques and optimizing distributed model training. (b) Core developer of the OpenFed framework.
Ecovacs Nanjing AI Research Institute, 2019.1-2019.8 (Intern)
SLAM: (a) Worked on Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) for autonomous robots, focusing on dense indoor environment construction for advanced sweeping robots, improving navigation and efficiency.
Tencent AI Lab, 2018.6-2018.12 (Intern)
Depth Fusion: (a) Developed depth fusion techniques for 3D face reconstruction using the iPhone depth camera, contributing to improvements in facial recognition and augmented reality applications.
Preprints & Publications
First author's preprints & publications:
All preprints & publications: 0
-
 arXiv
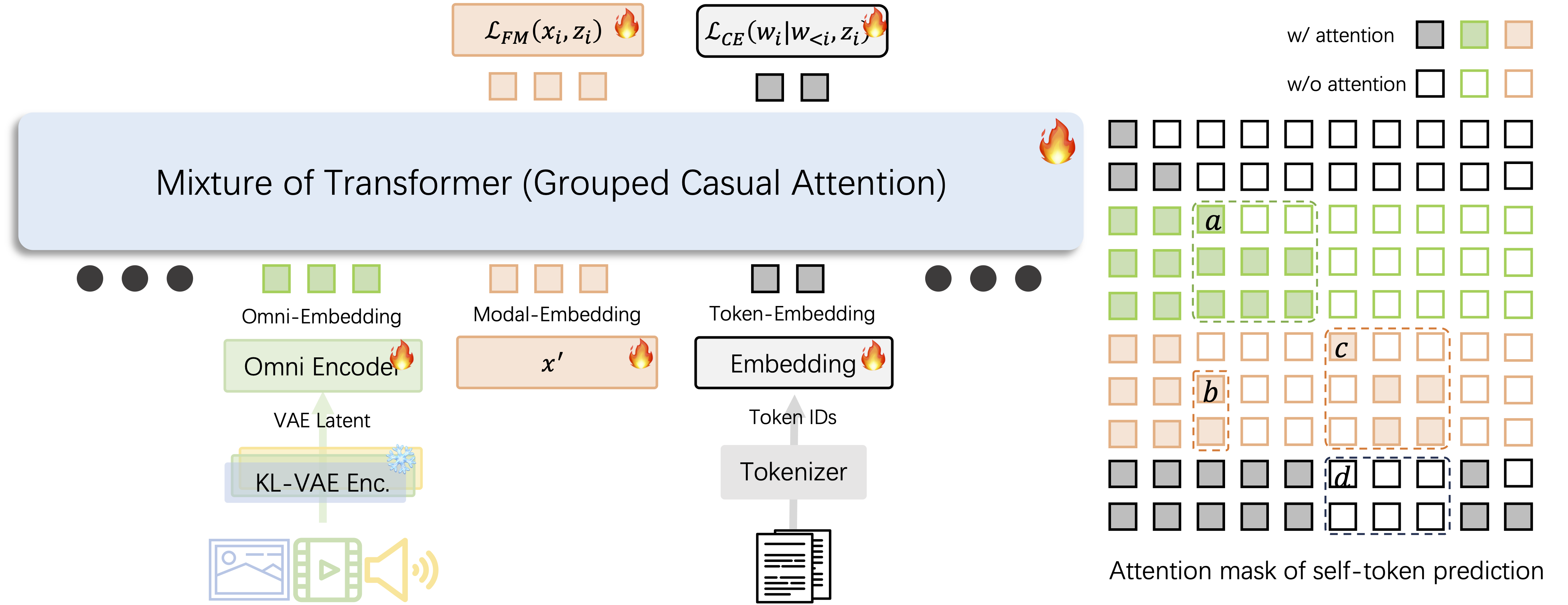
Abstract:Next-token prediction has been highly effective in language, but its extension to continuous modalities is challenging, regression over correlated latents tends to collapse into near-identity mappings, while discretization via vector-quantized encoders introduces quantization artifacts. Mask-based prediction with diffusion heads mitigates these issues, yet suffers from a train–inference mismatch, inability to use key–value caching, and poor scalability to long sequences. To overcome these limitations, we propose self-token prediction, which conditions each token on ground-truth references during training, ensuring consistency with causal inference while avoiding identity collapse. This design supports key–value caching and parallel generation, enabling scalable, high-fidelity synthesis across text, audio, image, and video. Built on this paradigm, OMNIAR unifies heterogeneous modalities in a shared omni-token space, achieving efficient and high-quality generation, including real-time and theoretically endless video generation1.
arXiv
Abstract:Next-token prediction has been highly effective in language, but its extension to continuous modalities is challenging, regression over correlated latents tends to collapse into near-identity mappings, while discretization via vector-quantized encoders introduces quantization artifacts. Mask-based prediction with diffusion heads mitigates these issues, yet suffers from a train–inference mismatch, inability to use key–value caching, and poor scalability to long sequences. To overcome these limitations, we propose self-token prediction, which conditions each token on ground-truth references during training, ensuring consistency with causal inference while avoiding identity collapse. This design supports key–value caching and parallel generation, enabling scalable, high-fidelity synthesis across text, audio, image, and video. Built on this paradigm, OMNIAR unifies heterogeneous modalities in a shared omni-token space, achieving efficient and high-quality generation, including real-time and theoretically endless video generation1. -
 arXiv
Abstract:Recently, autoregressive models have demonstrated remarkable performance in class-conditional image generation. However, the application of next-token prediction to high-resolution text-to-image generation remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we introduce \textbf{D-JEPA$\cdot$T2I}, an autoregressive model based on continuous tokens that incorporates innovations in both architecture and training strategy to generate high-quality, photorealistic images at arbitrary resolutions, up to 4K. Architecturally, we adopt the denoising joint embedding predictive architecture (D-JEPA) while leveraging a multimodal visual transformer to effectively integrate textual and visual features. Additionally, we introduce flow matching loss alongside the proposed Visual Rotary Positional Embedding (VoPE) to enable continuous resolution learning. In terms of training strategy, we propose a data feedback mechanism that dynamically adjusts the sampling procedure based on statistical analysis and an online learning critic model. This encourages the model to move beyond its comfort zone, reducing redundant training on well-mastered scenarios and compelling it to address more challenging cases with suboptimal generation quality. For the first time, we achieve state-of-the-art high-resolution image synthesis via next-token prediction.
arXiv
Abstract:Recently, autoregressive models have demonstrated remarkable performance in class-conditional image generation. However, the application of next-token prediction to high-resolution text-to-image generation remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we introduce \textbf{D-JEPA$\cdot$T2I}, an autoregressive model based on continuous tokens that incorporates innovations in both architecture and training strategy to generate high-quality, photorealistic images at arbitrary resolutions, up to 4K. Architecturally, we adopt the denoising joint embedding predictive architecture (D-JEPA) while leveraging a multimodal visual transformer to effectively integrate textual and visual features. Additionally, we introduce flow matching loss alongside the proposed Visual Rotary Positional Embedding (VoPE) to enable continuous resolution learning. In terms of training strategy, we propose a data feedback mechanism that dynamically adjusts the sampling procedure based on statistical analysis and an online learning critic model. This encourages the model to move beyond its comfort zone, reducing redundant training on well-mastered scenarios and compelling it to address more challenging cases with suboptimal generation quality. For the first time, we achieve state-of-the-art high-resolution image synthesis via next-token prediction. -
 ICLR
In The Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations.Abstract:Joint-embedding predictive architectures (JEPAs) have shown substantial promise in self-supervised representation learning, yet their application in generative modeling remains underexplored. Conversely, diffusion models have demonstrated significant efficacy in modeling arbitrary probability distributions. In this paper, we introduce Denoising with a Joint-Embedding Predictive Architecture (D-JEPA), pioneering the integration of JEPA within generative modeling. By recognizing JEPA as a form of masked image modeling, we reinterpret it as a generalized next-token prediction strategy, facilitating data generation in an autoregressive manner. Furthermore, we incorporate diffusion loss to model the pertoken probability distribution, enabling data generation in a continuous space. We also adapt flow matching loss as an alternative to diffusion loss, thereby enhancing the flexibility of D-JEPA. Empirically, with increased GFLOPs, D-JEPA consistently achieves lower FID scores with fewer training epochs, indicating its good scalability. Our base, large, and huge models outperform all previous generative models across all scales on ImageNet conditional generation benchmarks. Beyond image generation, D-JEPA is well-suited for other continuous data modeling, including video and audio.
ICLR
In The Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations.Abstract:Joint-embedding predictive architectures (JEPAs) have shown substantial promise in self-supervised representation learning, yet their application in generative modeling remains underexplored. Conversely, diffusion models have demonstrated significant efficacy in modeling arbitrary probability distributions. In this paper, we introduce Denoising with a Joint-Embedding Predictive Architecture (D-JEPA), pioneering the integration of JEPA within generative modeling. By recognizing JEPA as a form of masked image modeling, we reinterpret it as a generalized next-token prediction strategy, facilitating data generation in an autoregressive manner. Furthermore, we incorporate diffusion loss to model the pertoken probability distribution, enabling data generation in a continuous space. We also adapt flow matching loss as an alternative to diffusion loss, thereby enhancing the flexibility of D-JEPA. Empirically, with increased GFLOPs, D-JEPA consistently achieves lower FID scores with fewer training epochs, indicating its good scalability. Our base, large, and huge models outperform all previous generative models across all scales on ImageNet conditional generation benchmarks. Beyond image generation, D-JEPA is well-suited for other continuous data modeling, including video and audio. -
 arXiv
Abstract:Incorporating a temporal dimension into pretrained image diffusion models for video generation is a prevalent approach. However, this method is computationally demanding and necessitates large-scale video datasets. More critically, the heterogeneity between image and video datasets often results in catastrophic forgetting of the image expertise. Recent attempts to directly extract video snippets from image diffusion models have somewhat mitigated these problems. Nevertheless, these methods can only generate brief video clips with simple movements and fail to capture fine-grained motion or non-grid deformation. In this paper, we propose a novel Zero-Shot video Sampling algorithm, denoted as ZS2, capable of directly sampling high-quality video clips from existing image synthesis methods, such as Stable Diffusion, without any training or optimization. Specifically, ZS2 utilizes the dependency noise model and temporal momentum attention to ensure content consistency and animation coherence, respectively. This ability enables it to excel in related tasks, such as conditional and context-specialized video generation and instruction-guided video editing. Experimental results demonstrate that ZS2 achieves state-of-the-art performance in zero-shot video generation, occasionally outperforming recent supervised methods.
arXiv
Abstract:Incorporating a temporal dimension into pretrained image diffusion models for video generation is a prevalent approach. However, this method is computationally demanding and necessitates large-scale video datasets. More critically, the heterogeneity between image and video datasets often results in catastrophic forgetting of the image expertise. Recent attempts to directly extract video snippets from image diffusion models have somewhat mitigated these problems. Nevertheless, these methods can only generate brief video clips with simple movements and fail to capture fine-grained motion or non-grid deformation. In this paper, we propose a novel Zero-Shot video Sampling algorithm, denoted as ZS2, capable of directly sampling high-quality video clips from existing image synthesis methods, such as Stable Diffusion, without any training or optimization. Specifically, ZS2 utilizes the dependency noise model and temporal momentum attention to ensure content consistency and animation coherence, respectively. This ability enables it to excel in related tasks, such as conditional and context-specialized video generation and instruction-guided video editing. Experimental results demonstrate that ZS2 achieves state-of-the-art performance in zero-shot video generation, occasionally outperforming recent supervised methods. -
 arXiv
Abstract:The Gaussian diffusion model, initially designed for image generation, has recently been adapted for 3D point cloud generation. However, these adaptations have not fully considered the intrinsic geometric characteristics of 3D shapes, thereby constraining the diffusion model's potential for 3D shape manipulation. To address this limitation, we introduce a novel deformable 3D shape diffusion model that facilitates comprehensive 3D shape manipulation, including point cloud generation, mesh deformation, and facial animation. Our approach innovatively incorporates a differential deformation kernel, which deconstructs the generation of geometric structures into successive nonrigid deformation stages. By leveraging a probabilistic diffusion model to simulate this step-by-step process, our method provides a versatile and efficient solution for a wide range of applications, spanning from graphics rendering to facial expression animation. Empirical evidence highlights the effectiveness of our approach, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance in point cloud generation and competitive results in mesh deformation. Additionally, extensive visual demonstrations reveal the significant potential of our approach for practical applications. Our method presents a unique pathway for advancing 3D shape manipulation and unlocking new opportunities in the realm of virtual reality.
arXiv
Abstract:The Gaussian diffusion model, initially designed for image generation, has recently been adapted for 3D point cloud generation. However, these adaptations have not fully considered the intrinsic geometric characteristics of 3D shapes, thereby constraining the diffusion model's potential for 3D shape manipulation. To address this limitation, we introduce a novel deformable 3D shape diffusion model that facilitates comprehensive 3D shape manipulation, including point cloud generation, mesh deformation, and facial animation. Our approach innovatively incorporates a differential deformation kernel, which deconstructs the generation of geometric structures into successive nonrigid deformation stages. By leveraging a probabilistic diffusion model to simulate this step-by-step process, our method provides a versatile and efficient solution for a wide range of applications, spanning from graphics rendering to facial expression animation. Empirical evidence highlights the effectiveness of our approach, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance in point cloud generation and competitive results in mesh deformation. Additionally, extensive visual demonstrations reveal the significant potential of our approach for practical applications. Our method presents a unique pathway for advancing 3D shape manipulation and unlocking new opportunities in the realm of virtual reality. -
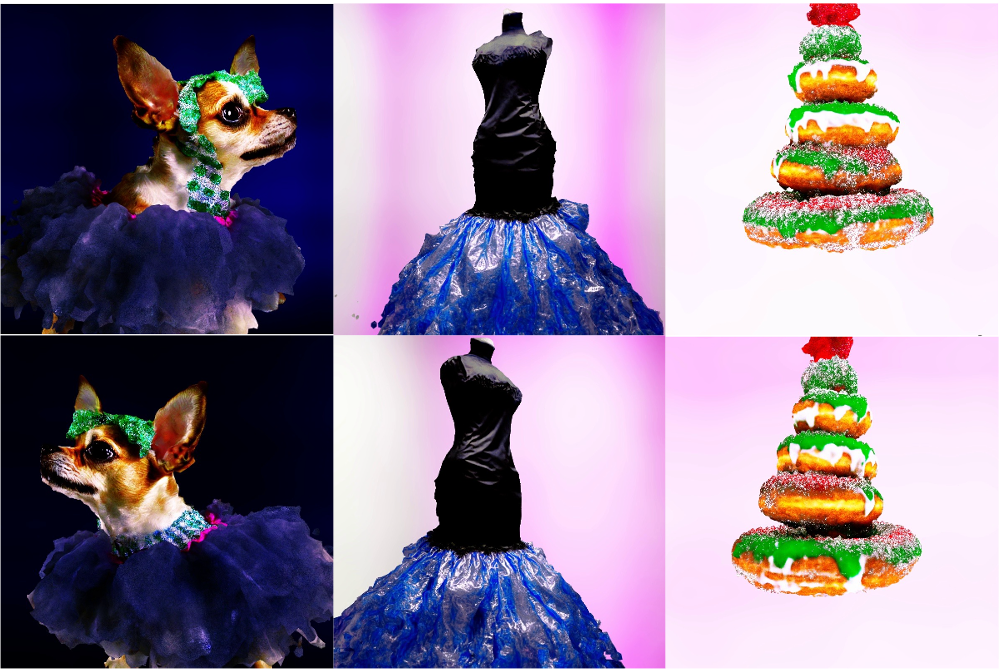
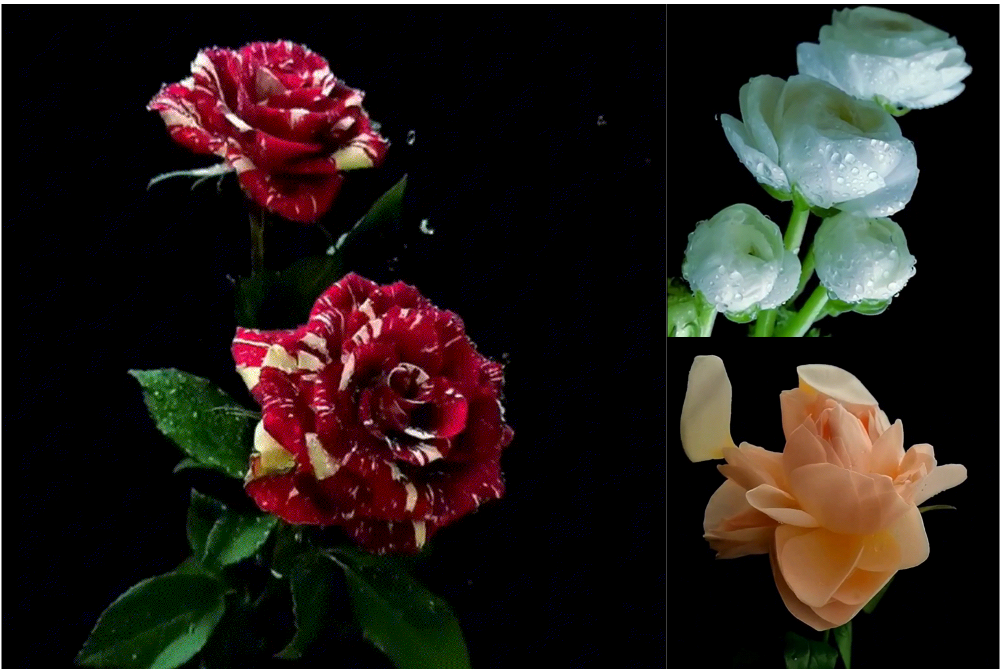 CVPR
In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 7131–7140, 2024.Abstract:We present the pioneering Large Visual Motion Model (LVMM), meticulously engineered to analyze the intrinsic dynamics encapsulated within real-world imagery. Our model, fortified with a wealth of prior knowledge extracted from billions of image pairs, demonstrates promising results in predicting a diverse spectrum of scene dynamics. As a result, it can infuse any generic image with authentic dynamic effects, enhancing its visual allure.
CVPR
In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 7131–7140, 2024.Abstract:We present the pioneering Large Visual Motion Model (LVMM), meticulously engineered to analyze the intrinsic dynamics encapsulated within real-world imagery. Our model, fortified with a wealth of prior knowledge extracted from billions of image pairs, demonstrates promising results in predicting a diverse spectrum of scene dynamics. As a result, it can infuse any generic image with authentic dynamic effects, enhancing its visual allure. -
 AAAI
In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pages 1028–1036, 2024.Abstract:Despite significant progress in utilizing pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models to guide the creation of 3D scenes, these methods often struggle to generate scenes that are sufficiently realistic, leading to 'neural scene degeneration'. In this work, we propose a new 3D scene generation model called Real3D. Specifically, Real3D designs a pipeline from a NeRF-like implicit renderer to a tetrahedrons-based explicit renderer, greatly improving the neural network's ability to generate various neural scenes. Moreover, Real3D introduces an additional discriminator to prevent neural scenes from falling into undesirable local optima, thus avoiding the degeneration phenomenon. Our experimental results demonstrate that Real3D outperforms all existing state-of-the-art text-to-3D generation methods, providing valuable insights to facilitate the development of learning-based 3D scene generation approaches.
AAAI
In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pages 1028–1036, 2024.Abstract:Despite significant progress in utilizing pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models to guide the creation of 3D scenes, these methods often struggle to generate scenes that are sufficiently realistic, leading to 'neural scene degeneration'. In this work, we propose a new 3D scene generation model called Real3D. Specifically, Real3D designs a pipeline from a NeRF-like implicit renderer to a tetrahedrons-based explicit renderer, greatly improving the neural network's ability to generate various neural scenes. Moreover, Real3D introduces an additional discriminator to prevent neural scenes from falling into undesirable local optima, thus avoiding the degeneration phenomenon. Our experimental results demonstrate that Real3D outperforms all existing state-of-the-art text-to-3D generation methods, providing valuable insights to facilitate the development of learning-based 3D scene generation approaches. -
 CVPR
In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 12187–12197, 2023.Abstract:Federated learning enables the privacy-preserving training of neural network models using real-world data across distributed clients. FedAvg has become the preferred optimizer for federated learning because of its simplicity and effectiveness. FedAvg uses naïve aggregation to update the server model, interpolating client models based on the number of instances used in their training. However, naïve aggregation suffers from client drift when the data is heterogenous (non-IID), leading to unstable and slow convergence. In this work, we propose a novel aggregation approach, elastic aggregation, to overcome these issues. Elastic aggregation interpolates client models adaptively according to parameter sensitivity, which is measured by computing how much the overall prediction function output changes when each parameter is changed. This measurement is performed in an unsupervised and online manner. Elastic aggregation reduces the magnitudes of updates to the more sensitive parameters so as to prevent the server model from drifting to any one client distribution, and conversely boosts updates to the less sensitive parameters to better explore different client distributions. Empirical results on real and synthetic data as well as analytical results show that elastic aggregation leads to efficient training in both convex and non-convex settings while being fully agnostic to client heterogeneity and robust to large numbers of clients, partial participation, and imbalanced data. Finally, elastic aggregation works well with other federated optimizers and achieves significant improvements across the board.
CVPR
In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 12187–12197, 2023.Abstract:Federated learning enables the privacy-preserving training of neural network models using real-world data across distributed clients. FedAvg has become the preferred optimizer for federated learning because of its simplicity and effectiveness. FedAvg uses naïve aggregation to update the server model, interpolating client models based on the number of instances used in their training. However, naïve aggregation suffers from client drift when the data is heterogenous (non-IID), leading to unstable and slow convergence. In this work, we propose a novel aggregation approach, elastic aggregation, to overcome these issues. Elastic aggregation interpolates client models adaptively according to parameter sensitivity, which is measured by computing how much the overall prediction function output changes when each parameter is changed. This measurement is performed in an unsupervised and online manner. Elastic aggregation reduces the magnitudes of updates to the more sensitive parameters so as to prevent the server model from drifting to any one client distribution, and conversely boosts updates to the less sensitive parameters to better explore different client distributions. Empirical results on real and synthetic data as well as analytical results show that elastic aggregation leads to efficient training in both convex and non-convex settings while being fully agnostic to client heterogeneity and robust to large numbers of clients, partial participation, and imbalanced data. Finally, elastic aggregation works well with other federated optimizers and achieves significant improvements across the board. -
 CVPR
In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 5018–5026, 2023.Abstract:Recent developments in Artificial Intelligence techniques have enabled their successful application across a spectrum of commercial and industrial settings. However, these techniques require large volumes of data to be aggregated in a centralized manner, forestalling their applicability to scenarios wherein the data is sensitive or the cost of data transmission is prohibitive. Federated Learning alleviates these problems by decentralizing model training, thereby removing the need for data transfer and aggregation. To advance the adoption of Federated Learning, more research and development needs to be conducted to address some important open questions. In this work, we propose OpenFed, an open-source software framework for end-to-end Federated Learning. OpenFed reduces the barrier to entry for both researchers and downstream users of Federated Learning by the targeted removal of existing pain points. For researchers, OpenFed provides a framework wherein new methods can be easily implemented and fairly evaluated against an extensive suite of benchmarks. For downstream users, OpenFed allows Federated Learning to be plugged and play within different subject-matter contexts, removing the need for deep expertise in Federated Learning.
CVPR
In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 5018–5026, 2023.Abstract:Recent developments in Artificial Intelligence techniques have enabled their successful application across a spectrum of commercial and industrial settings. However, these techniques require large volumes of data to be aggregated in a centralized manner, forestalling their applicability to scenarios wherein the data is sensitive or the cost of data transmission is prohibitive. Federated Learning alleviates these problems by decentralizing model training, thereby removing the need for data transfer and aggregation. To advance the adoption of Federated Learning, more research and development needs to be conducted to address some important open questions. In this work, we propose OpenFed, an open-source software framework for end-to-end Federated Learning. OpenFed reduces the barrier to entry for both researchers and downstream users of Federated Learning by the targeted removal of existing pain points. For researchers, OpenFed provides a framework wherein new methods can be easily implemented and fairly evaluated against an extensive suite of benchmarks. For downstream users, OpenFed allows Federated Learning to be plugged and play within different subject-matter contexts, removing the need for deep expertise in Federated Learning. -
 ICLR
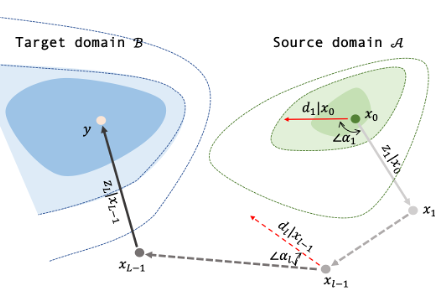
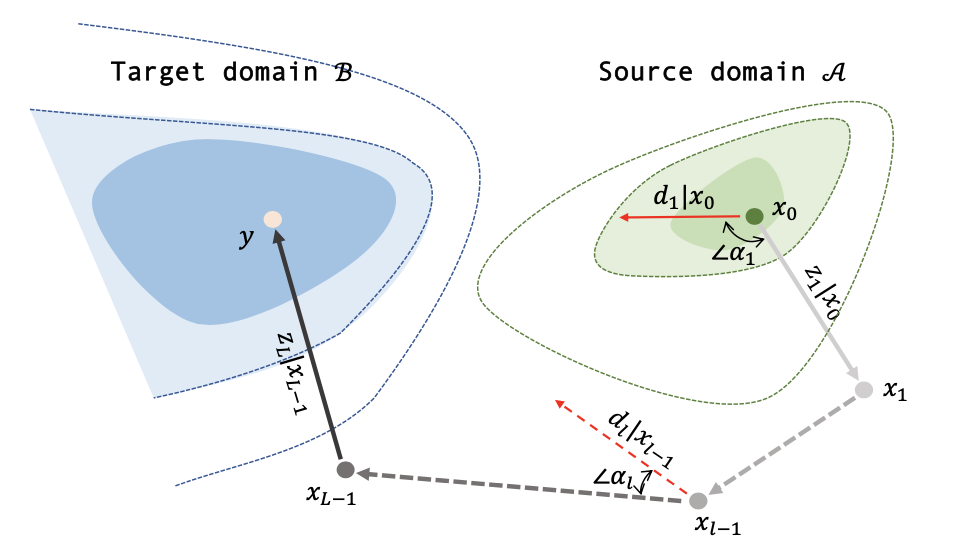
In The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations.Abstract:Over the past few years afterward the birth of ResNet, skip connection has become the defacto standard for the design of modern architectures due to its widespread adoption, easy optimization, and proven performance. Prior work has explained the effectiveness of the skip connection mechanism from different perspectives. In this work, we deep dive into the model's behaviors with skip connections which can be formulated as a learnable Markov chain. An efficient Markov chain is preferred as it always maps the input data to the target domain in a better way. However, while a model is explained as a Markov chain, it is not guaranteed to be optimized following an efficient Markov chain by existing SGD-based optimizers prone to getting trapped in local optimal points. In order to move towards a more efficient Markov chain, we propose a simple routine of penal connection to make any residual-like model become a learnable Markov chain. Aside from that, the penal connection can also be viewed as a particular model regularization and can be easily implemented with one line of code in the most popular deep learning frameworks. The encouraging experimental results in multi-modal translation and image recognition empirically confirm our conjecture of the learnable Markov chain view and demonstrate the superiority of the proposed penal connection.
ICLR
In The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations.Abstract:Over the past few years afterward the birth of ResNet, skip connection has become the defacto standard for the design of modern architectures due to its widespread adoption, easy optimization, and proven performance. Prior work has explained the effectiveness of the skip connection mechanism from different perspectives. In this work, we deep dive into the model's behaviors with skip connections which can be formulated as a learnable Markov chain. An efficient Markov chain is preferred as it always maps the input data to the target domain in a better way. However, while a model is explained as a Markov chain, it is not guaranteed to be optimized following an efficient Markov chain by existing SGD-based optimizers prone to getting trapped in local optimal points. In order to move towards a more efficient Markov chain, we propose a simple routine of penal connection to make any residual-like model become a learnable Markov chain. Aside from that, the penal connection can also be viewed as a particular model regularization and can be easily implemented with one line of code in the most popular deep learning frameworks. The encouraging experimental results in multi-modal translation and image recognition empirically confirm our conjecture of the learnable Markov chain view and demonstrate the superiority of the proposed penal connection. -
 arXiv
Abstract:Element-wise activation functions play a critical role in deep neural networks via affecting the expressivity power and the learning dynamics. Learning-based activation functions have recently gained increasing attention and success. We propose a new perspective of learnable activation function through formulating them with element-wise attention mechanism. In each network layer, we devise an attention module which learns an element-wise, sign-based attention map for the pre-activation feature map. The attention map scales an element based on its sign. Adding the attention module with a rectified linear unit (ReLU) results in an amplification of positive elements and a suppression of negative ones, both with learned, data-adaptive parameters. We coin the resulting activation function Attention-based Rectified Linear Unit (AReLU). The attention module essentially learns an element-wise residue of the activated part of the input, as ReLU can be viewed as an identity transformation. This makes the network training more resistant to gradient vanishing. The learned attentive activation leads to well-focused activation of relevant regions of a feature map. Through extensive evaluations, we show that AReLU significantly boosts the performance of most mainstream network architectures with only two extra learnable parameters per layer introduced. Notably, AReLU facilitates fast network training under small learning rates, which makes it especially suited in the case of transfer learning and meta learning.
arXiv
Abstract:Element-wise activation functions play a critical role in deep neural networks via affecting the expressivity power and the learning dynamics. Learning-based activation functions have recently gained increasing attention and success. We propose a new perspective of learnable activation function through formulating them with element-wise attention mechanism. In each network layer, we devise an attention module which learns an element-wise, sign-based attention map for the pre-activation feature map. The attention map scales an element based on its sign. Adding the attention module with a rectified linear unit (ReLU) results in an amplification of positive elements and a suppression of negative ones, both with learned, data-adaptive parameters. We coin the resulting activation function Attention-based Rectified Linear Unit (AReLU). The attention module essentially learns an element-wise residue of the activated part of the input, as ReLU can be viewed as an identity transformation. This makes the network training more resistant to gradient vanishing. The learned attentive activation leads to well-focused activation of relevant regions of a feature map. Through extensive evaluations, we show that AReLU significantly boosts the performance of most mainstream network architectures with only two extra learnable parameters per layer introduced. Notably, AReLU facilitates fast network training under small learning rates, which makes it especially suited in the case of transfer learning and meta learning. -
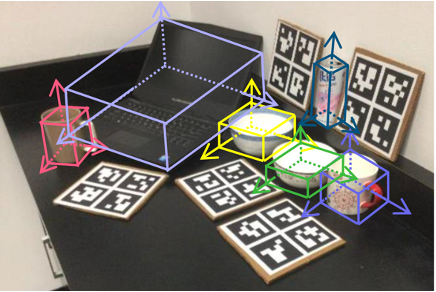 CVPR
In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 11973–11982, 2020.Abstract:We present a novel approach to category-level 6D object pose and size estimation. To tackle intra-class shape variations, we learn canonical shape space (CASS), a unified representation for a large variety of instances of a certain object category. In particular, CASS is modeled as the latent space of a deep generative model of canonical 3D shapes with normalized pose. We train a variational auto-encoder (VAE) for generating 3D point clouds in the canonical space from an RGBD image. The VAE is trained in a cross-category fashion, exploiting the publicly available large 3D shape repositories. Since the 3D point cloud is generated in normalized pose (with actual size), the encoder of the VAE learns view-factorized RGBD embedding. It maps an RGBD image in arbitrary view into a pose-independent 3D shape representation. Object pose is then estimated via contrasting it with a pose-dependent feature of the input RGBD extracted with a separate deep neural networks. We integrate the learning of CASS and pose and size estimation into an end-to-end trainable network, achieving the state-of-the-art performance.
CVPR
In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 11973–11982, 2020.Abstract:We present a novel approach to category-level 6D object pose and size estimation. To tackle intra-class shape variations, we learn canonical shape space (CASS), a unified representation for a large variety of instances of a certain object category. In particular, CASS is modeled as the latent space of a deep generative model of canonical 3D shapes with normalized pose. We train a variational auto-encoder (VAE) for generating 3D point clouds in the canonical space from an RGBD image. The VAE is trained in a cross-category fashion, exploiting the publicly available large 3D shape repositories. Since the 3D point cloud is generated in normalized pose (with actual size), the encoder of the VAE learns view-factorized RGBD embedding. It maps an RGBD image in arbitrary view into a pose-independent 3D shape representation. Object pose is then estimated via contrasting it with a pose-dependent feature of the input RGBD extracted with a separate deep neural networks. We integrate the learning of CASS and pose and size estimation into an end-to-end trainable network, achieving the state-of-the-art performance. -
Abstract:Recently, various convolutions based on continuous or discrete kernels for point cloud processing have been widely studied, and achieve impressive performance in many applications, such as shape classification, scene segmentation and so on. However, they still suffer from some drawbacks. For continuous kernels, the inaccurate estimation of the kernel weights constitutes a bottleneck for further improving the performance; while for discrete ones, the kernels represented as the points located in the 3D space are lack of rich geometry information. In this work, rather than defining a continuous or discrete kernel, we directly embed convolutional kernels into the learnable potential fields, giving rise to potential convolution. It is convenient for us to define various potential functions for potential convolution which can generalize well to a wide range of tasks. Specifically, we provide two simple yet effective potential functions via point-wise convolution operations. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, which achieves superior performance on the popular 3D shape classification and scene segmentation benchmarks compared with other state-of-the-art point convolution methods.
-
 TIP
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 28(8):3766–3777, 2019.Abstract:The tracking-by-detection framework receives growing attentions through the integration with the Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). Existing tracking-by-detection based methods, however, fail to track objects with severe appearance variations. This is because the traditional convolutional operation is performed on fixed grids, and thus may not be able to find the correct response while the object is changing pose or under varying environmental conditions. In this paper, we propose a deformable convolution layer to enrich the target appearance representations in the tracking-by-detection framework. We aim to capture the target appearance variations via deformable convolution, which adaptively enhances its original features. In addition, we also propose a gated fusion scheme to control how the variations captured by the deformable convolution affect the original appearance. The enriched feature representation through deformable convolution facilitates the discrimination of the CNN classifier on the target object and background. Extensive experiments on the standard benchmarks show that the proposed tracker performs favorably against state-of-the-art methods.
TIP
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 28(8):3766–3777, 2019.Abstract:The tracking-by-detection framework receives growing attentions through the integration with the Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). Existing tracking-by-detection based methods, however, fail to track objects with severe appearance variations. This is because the traditional convolutional operation is performed on fixed grids, and thus may not be able to find the correct response while the object is changing pose or under varying environmental conditions. In this paper, we propose a deformable convolution layer to enrich the target appearance representations in the tracking-by-detection framework. We aim to capture the target appearance variations via deformable convolution, which adaptively enhances its original features. In addition, we also propose a gated fusion scheme to control how the variations captured by the deformable convolution affect the original appearance. The enriched feature representation through deformable convolution facilitates the discrimination of the CNN classifier on the target object and background. Extensive experiments on the standard benchmarks show that the proposed tracker performs favorably against state-of-the-art methods. -
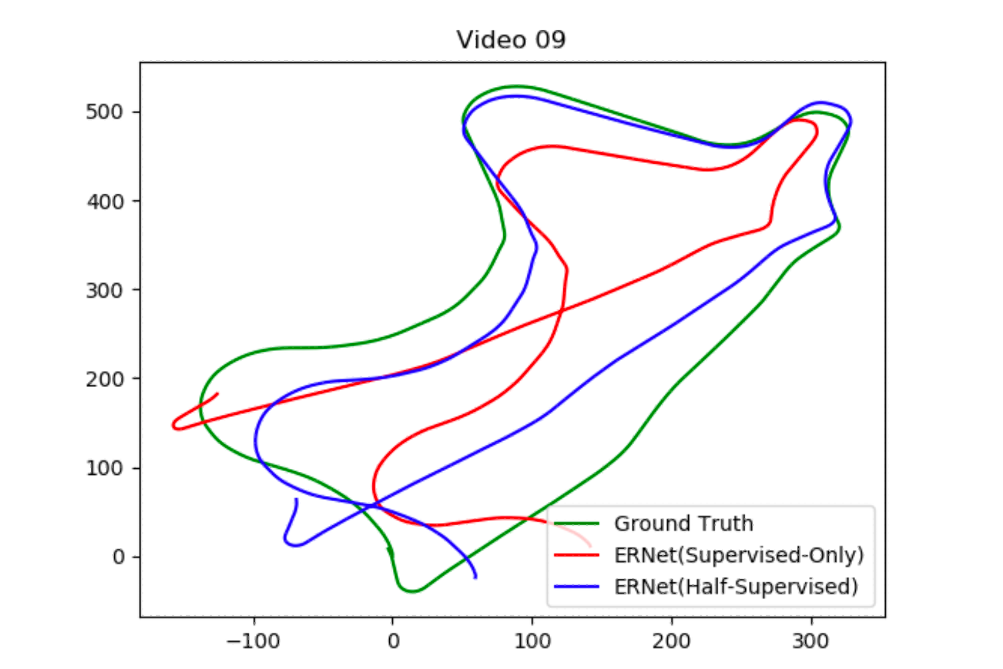 IROS
International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2019Abstract:In the last decade, supervised deep learning approaches have extensively employed in visual odometry (VO) applications, which is not feasible in environments where labelled data is not abundant. Therefore, many unsupervised deep learning approaches based on depth map in unknown environments from unlabeled data have been proposed. In this paper, we propose a more simplify framework (Encode and Regress Network, ERNet) to generate a robust 6-DoF pose of a monocular camera with Semi-supervised learning strategy. Compared to other state of the art unsupervised deep VO methods, our framework without any assistant of depth map information can also achieve a good performance in terms of pose accuracy on KITTI dataset.
IROS
International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2019Abstract:In the last decade, supervised deep learning approaches have extensively employed in visual odometry (VO) applications, which is not feasible in environments where labelled data is not abundant. Therefore, many unsupervised deep learning approaches based on depth map in unknown environments from unlabeled data have been proposed. In this paper, we propose a more simplify framework (Encode and Regress Network, ERNet) to generate a robust 6-DoF pose of a monocular camera with Semi-supervised learning strategy. Compared to other state of the art unsupervised deep VO methods, our framework without any assistant of depth map information can also achieve a good performance in terms of pose accuracy on KITTI dataset. -
 ROBIO
In 2019 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), pages 2914–2919. IEEE, 2019.Abstract:Traditional CNN-based recognition algorithms are trained for limited labeled data, which may not perform well in a different environment due to the lack of adaptivity of the CNN networks. So the traditional CNN-based recognition algorithms can not play a good role in robot applications because the robots have to work in different environments. However, the robot can continuously perceive new images during its mission. These images contain lots of environment-related features but lack of labels. So the robots must learn the environment-related features adaptively with unlabeled data to further improve the performance of CNN-based recognition algorithms. We call this ability as active object recognition (OBR). In this paper, we designed a dynamic memory structure (DMS) which can adaptively learn the environment-related features online and embedded DMS into a VGG-16 network to implement active object recognition. We also evaluate our dynamic memory network of CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 classification dataset. The results show that by learning environment-related features, dynamic memory network achieves a better performance on classification accuracy. More importantly, the network can have the ability to improve itself while many times testing.
ROBIO
In 2019 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), pages 2914–2919. IEEE, 2019.Abstract:Traditional CNN-based recognition algorithms are trained for limited labeled data, which may not perform well in a different environment due to the lack of adaptivity of the CNN networks. So the traditional CNN-based recognition algorithms can not play a good role in robot applications because the robots have to work in different environments. However, the robot can continuously perceive new images during its mission. These images contain lots of environment-related features but lack of labels. So the robots must learn the environment-related features adaptively with unlabeled data to further improve the performance of CNN-based recognition algorithms. We call this ability as active object recognition (OBR). In this paper, we designed a dynamic memory structure (DMS) which can adaptively learn the environment-related features online and embedded DMS into a VGG-16 network to implement active object recognition. We also evaluate our dynamic memory network of CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 classification dataset. The results show that by learning environment-related features, dynamic memory network achieves a better performance on classification accuracy. More importantly, the network can have the ability to improve itself while many times testing. -
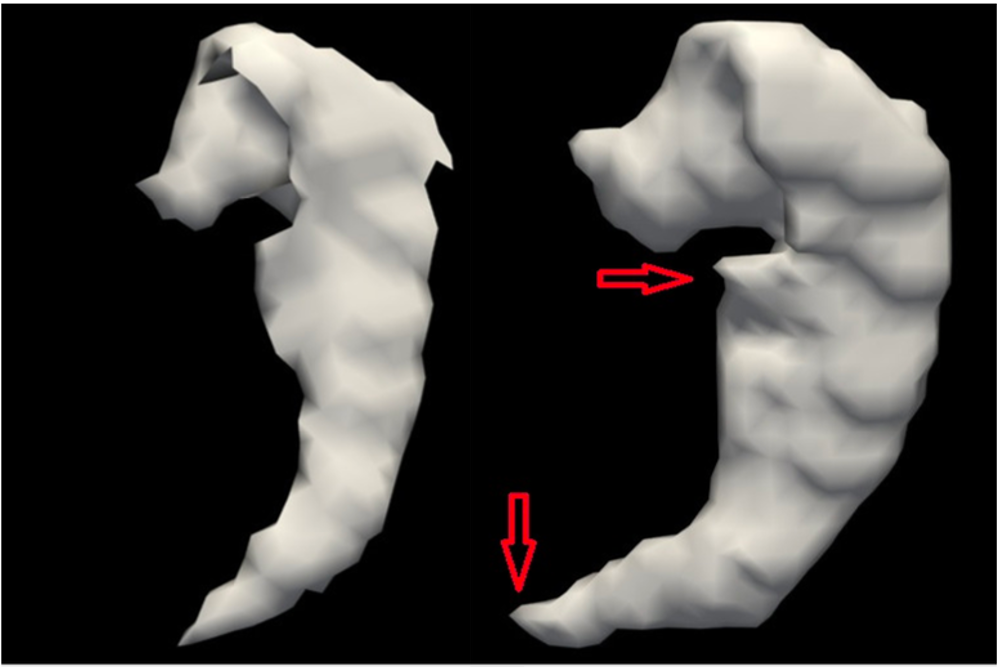 ICIA
In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation (ICIA), pages 455–460. IEEE, 2018Abstract:Detection and segmentation of the hippocampal structures in volumetric brain images is a challenging problem in the area of medical imaging. In this paper, we propose a two-stage 3D fully convolutional neural network that efficiently detects and segments the hippocampal structures. In particular, our approach first localizes the hippocampus from the whole volumetric image and obtains a rough segmentation. This initial segmentation can be used an enhancement mask to extract the fine structure of the hippocampus. The proposed method has been evaluated on a public dataset and compared with state-of-the-art approaches. Results indicate the effectiveness of the proposed method, which yields mean Dice Similarity Coefficients(i.e. DSC) of 0.897 and 0.900 for the left and right hippocampus, respectively. Furthermore, extensive experiments manifest that the proposed enhancement mask layer has remarkable benefits for accelerating training process and obtaining more accurate segmentation results.
ICIA
In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation (ICIA), pages 455–460. IEEE, 2018Abstract:Detection and segmentation of the hippocampal structures in volumetric brain images is a challenging problem in the area of medical imaging. In this paper, we propose a two-stage 3D fully convolutional neural network that efficiently detects and segments the hippocampal structures. In particular, our approach first localizes the hippocampus from the whole volumetric image and obtains a rough segmentation. This initial segmentation can be used an enhancement mask to extract the fine structure of the hippocampus. The proposed method has been evaluated on a public dataset and compared with state-of-the-art approaches. Results indicate the effectiveness of the proposed method, which yields mean Dice Similarity Coefficients(i.e. DSC) of 0.897 and 0.900 for the left and right hippocampus, respectively. Furthermore, extensive experiments manifest that the proposed enhancement mask layer has remarkable benefits for accelerating training process and obtaining more accurate segmentation results.
Powered by Jekyll and Minimal Light theme.
 arXiv
arXiv